Vasectomy is a small procedure performed in the office of Best Urologist in Karachi for male birth control. This safe procedure involves cutting and sealing the tubes carrying sperms from the testes to the urethra. Although this is generally a safe procedure, there can be certain side-effects like post-vasectomy pain syndrome (PVPS). Read on to know more about PVPS including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment options:
What is PVPS?
As mentioned before, vasectomy involves interruption of the passage of sperms from the vas deferens to the urethra and the ejaculatory duct. In normal conditions, the sperm mixes with the seminal and prostatic fluids, and is ejaculated through the urethra in the penis during sexual climax. This pathway is interrupted through the procedure of vasectomy.
Vasectomy is an outpatient procedure whereby the vas deferens is blocked or cut, to interrupt the pathway of sperm. Since no sperm is then transferred to the urethra, the ejaculate cannot cause pregnancy. The man can still have normal sexual relations, ejaculate and climax normally.
Even though it is mostly a safe procedure, sometimes complications like PVPS can arise. The incidence of PVPS is about 1 in 100 cases. Every year about 0.5 million men undergo vasectomies, and the number of complications in these people is very low.
PVPS involves having chronic pain in one or both the testicles following the procedure, for a period of about three months or longer. This pain can develop either immediately following the procedure, or even months to years later. The character of the pain can vary from dull to sharp and persistent.
What Are The Symptoms Of PVPS?
The symptoms of pain in PVPS include:
- Pain during sexual activity
- Pain and tenderness in the genital area
- Dull ache in the testes
- Pain at the site of vasectomy
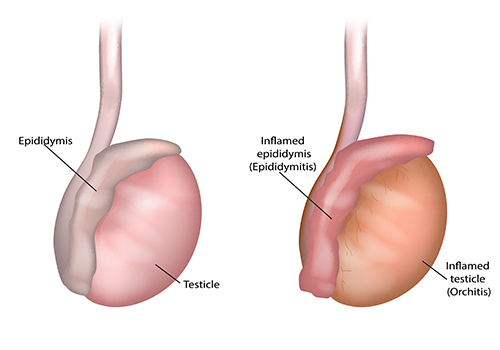
- Swelling in the epididymis (epididymitis)
- Pressure during climax and ejaculation
What causes PVPS?
The causes of PVPS include:
- Scarring: formation of scar tissue or adhesions at the surgical site of cutting of vas deferens can cause persistent pain.
- Nerve compression: if the nerves to the testicles gets involved, it may cause continuous pain after the procedure.
- Infection: inflammation anywhere along the surgical site and the pathway of the epididymis can cause PVPS.
- Back pressure: when the sperms are unable to travel from the testicle to the vas deferens as seen with vasectomy, they may cause back pressure and pain due to interrupted pathway.
What Conditions Are Similar To PVPS?
Sometimes, the pain itself it not secondary to PVPS. Rather other conditions can mimic PVPS, and these include:
- Hydrocele
- Inguinal hernia
- UTIs
- Testicular torsion
- Varicocele
- Metastatic tumors
- Testicular cancers
How is PVPS Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of PVPS is more of exclusion, based on thorough history and physical examination. There is no single investigation that can help make the diagnosis of PVPS. Investigations that support the diagnosis, include:
- Imaging tests like ultrasound
- Urinalysis including urine culture
- Semen analysis and culture
- Spermatic cord block
- Screening for sexually transmitted infections (STIs)
- Complete blood count to check for signs of infection
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan uses powerful radio waves to produce detailed images of the structures in the groin to rule out nerve compression.
What Are The Treatment Options For PVPS?
The medical and conservative therapy for PVPS includes:
- Supportive underwear: wearing compression shorts and jock straps can relieve pressure on the testicles and reduce pain.
- Physical therapy: pelvic floor exercises and physical therapy can teach the patient to relax the muscles of the pelvic floor to relieve pain.
- Icing and heating: alternate heating and icing of the genital area can relieve the pain of the involved region. In case of a flare-up, sitting in a warm bath can be helpful.
- Pain relievers: medications like ibuprofen and NSAIDs can help to reduce the inflammation of the involved area and treat pain.
- Antidepressants: these drugs help mitigate nerve pain in PVPS.
What Are The Complications Of PVPS?
PVPS is associated with significant distress for the patient which can impact the quality of life. Some men are unable to perform activities of daily living and sexual activity. Such men need expert help available at Reliance Hospital.